Russia intends to remain at the forefront of all innovations in global cosmonautics and regain its leadership in rocket launches. New promising developments will help in this, some of which are being conducted without publicizing information about them in the media.
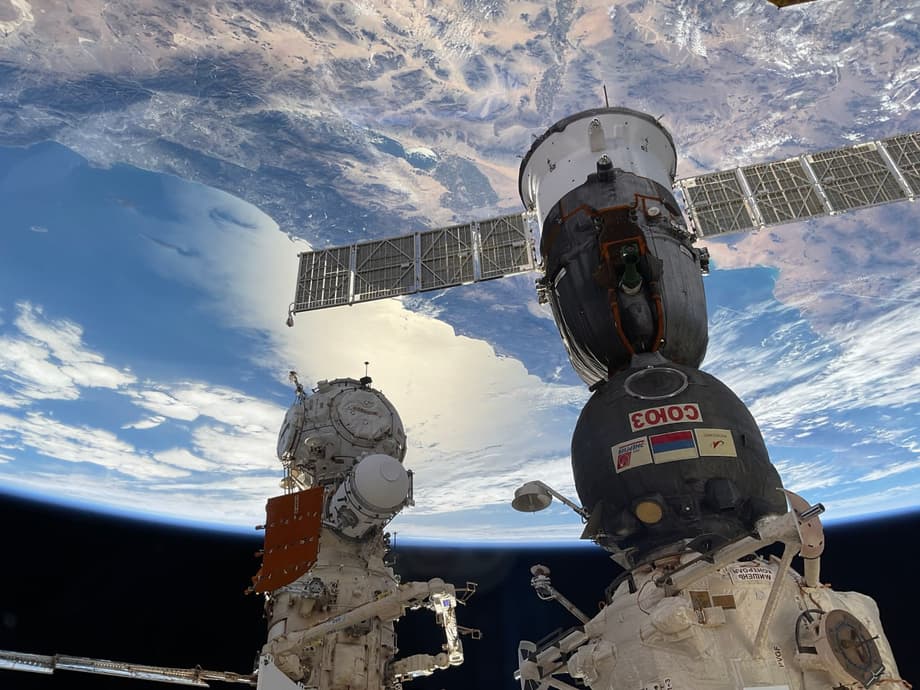

This was stated by the head of Roscosmos, Yuri Borisov, in an interview with the publication "Pro Kosmos". As Borisov noted, after taking office, he discovered that "the industry lacks a coherent technical policy, long-term in all areas - in satellite construction, in rocket construction, in scientific space, in the manned program".
The uncertainty of prospects and goals of work led employees of specialized enterprises into a state of "some confusion". However, now Roscosmos has a long-term development strategy.
"First Technical" has selected the main points from the interview with the head of Roscosmos. New Russian space plans - from special orders from the Ministry of Defense and reusable rockets to satellite assembly lines and the ROS.

"Amur-SPG" instead of "Soyuz"
Currently, launches are carried out by R7 family launch vehicles - "Soyuz", as well as "Protons", which are almost not used, and "Angara", which, as Borisov correctly said, is "also not a young development". In addition, it is mainly used "for launching military satellites".
The park of launch vehicles is planned to be updated by 2028-2029. RCC Progress is already actively working on the promising reusable carrier "Amur-SPG" with a multi-engine power plant. For it, as is known, an experimental oxygen-methane engine RD-0177 is being developed at the Voronezh KBKhA. The 100-ton thrust engine is planned to be fully completed by the end of 2025. Liquefied natural gas methane was chosen as fuel due to its efficiency and minimal soot formation.
If this work is successful, we hope that we can replicate it and use the design solutions incorporated in this rocket for a super-heavy carrier.
Special Order from the Ministry of Defense
This is an absolutely innovative ultra-light reusable carrier, which also runs on liquefied natural gas. It will ensure the profitability of launch services. TsNIIMash has "quite serious hopes" for this development.
The second customer of this promising carrier is the Foundation for Advanced Research. Work on the ultra-light carrier has been underway for "two or three years".
The work was not publicized, as this carrier is quite innovative in its design and technological solutions, new alloys and composite materials are used there. Tests of experimental stages of the future carrier were, in principle, successful, which proves the correctness of the design solutions. Today we are interested in the manufacture of engines and confirmation of the characteristics that are incorporated in them. If everything goes successfully, we will accelerate this work.
It is assumed that the carrier will be able to take off not only from cosmodromes, and will not cost as much as the carriers that already exist in Russia.
Satellite Construction and Assembly Lines
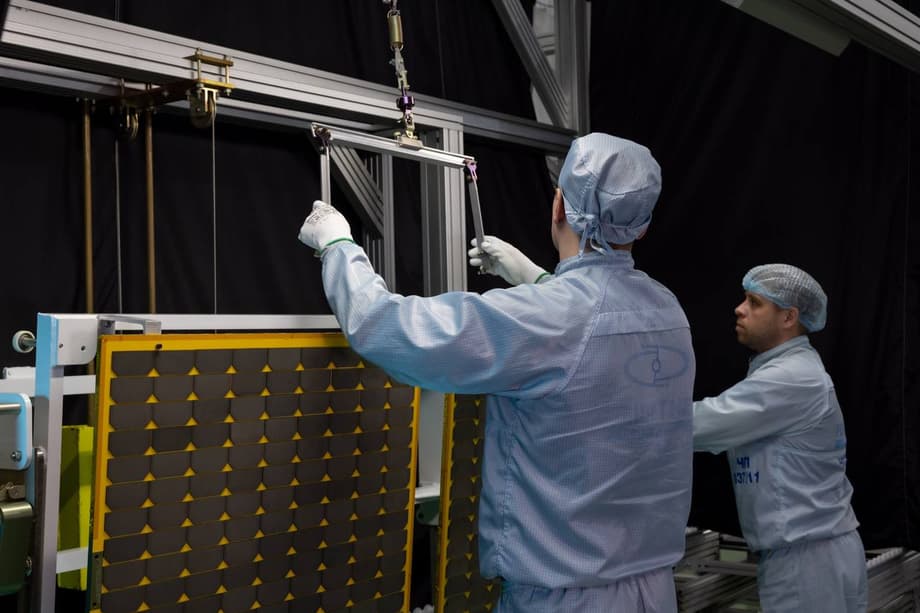

In order not to lag behind in space exploration and to build the Russian satellite constellation faster, it is necessary to accelerate their production. The first sign is already there - specialists of JSC "RESHETNEV" have developed an assembly line for small satellites.
This is a serious experience, it needs to be replicated. This assembly line is designed for assembling satellites weighing up to 100 kilograms, and we need to create an assembly line for devices up to 500 kilograms, this is other technological equipment and requires real costs. For which we, in fact, have planned about 50 billion rubles.
In addition, as "First Technical" has already written, "RESHETNEV" is working on new materials for satellite construction. And recently, its engineers and designers presented a new unified domestic platform for spacecraft weighing up to 1,000 kg. In one launch, the platform will be able to put up to four satellites into low circular orbits.
Universities are also involved in satellite construction - in particular, Novosibirsk State University helps to build "Griffons". This is a survey group of 132 CubeSat-type satellites with a resolution of about 2.5 meters. "Griffon" is part of the program to create a satellite constellation "Sphere", which involves launching 162 devices into orbit for monitoring the environment and mining, and regulating traffic flows.
Commercial Launches
Roscosmos is actively working to ensure that a space services market appears in the country. The first reading in the State Duma of the law on the commercialization of space services has already passed, and it may come into force on January 1, 2025. Then launches will cease to be free, and business structures will be able to participate in satellite construction and launches.
Without this law, as Borisov has repeatedly said, it is impossible to develop the Russian orbital constellation solely with state resources. By 2030, if the law comes into force, private companies will help with the launch of about 600 satellites, which is about 40% of the planned volume of the orbital constellation. Roscosmos is already conducting discussions on partnerships in this area with private companies.
As for the participation of private individuals in the creation of low-orbit multi-satellite constellations, the mechanism here is as follows: forward contracts are concluded with these companies, which guarantee them that their work will not be in vain, that if they produce devices with the characteristics that were declared, then Roscosmos, through the mechanism of forward contracts, begins to buy them out.
However, even with this, private individuals need state support for their innovations. Without subsidizing interest rates, additional tax benefits will be difficult for them - as Borisov recalled, Elon Musk with his business firmly stands on his feet thanks to solid Pentagon contracts.
Roscosmos, even taking into account the commercialization of the market, will still retain the exclusive key function of launching all spacecraft.
We do not yet have private companies capable of creating rocket technology and carrying out space launches. We have not seen companies like SpaceX. Although such business projects, as I know, are beginning to be born on an initiative basis at the startup stage. God grant them success in this area.
In addition to allowing private companies into the market, Roscosmos will receive financial support of another kind. At a meeting of the government commission on legislative activity, a draft federal law was approved, which will give the state corporation the opportunity to engage in advertising. This means that, for example, on space rockets or space infrastructure facilities, you can see advertising for cars, drinks, or some other business that operates within the framework of the law.
Russia's Partners in Space
According to Borisov, previously up to 70% of external contracts in space projects were built with European countries and the USA. Now they are practically "reduced to zero" - excluding work on the ISS and "cooperation in terms of ensuring the safety of space activities" with NASA for mutual assistance in space.
China has taken the vacant place - it is now the "main partner in long-term space projects" and is working with Russia on the lunar program. This includes, in particular, the project of the International Scientific Lunar Station. A range of BRICS countries may also join the Russian space partners - they have already expressed interest in consolidating efforts in the field of providing space services. In the future, this may result in the creation of a unified satellite constellation.
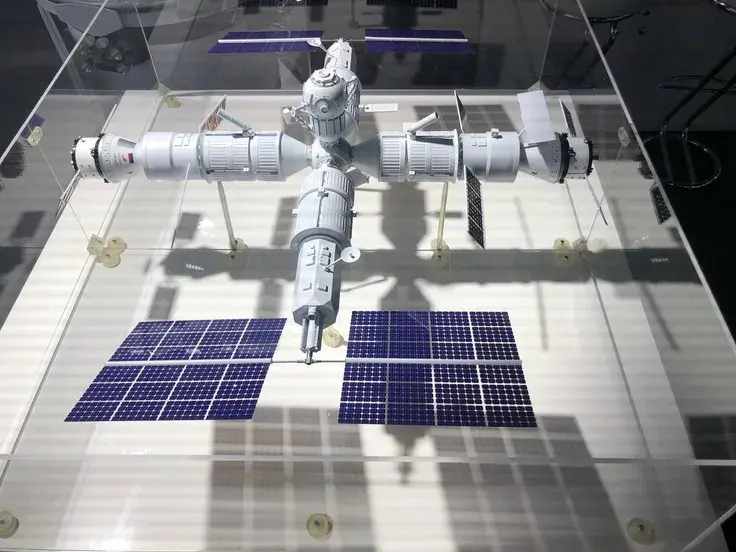
In addition, Russia intends to involve the BRICS countries in the development of the ROS - Russian Orbital Station. They have an interest in the project - not only because of the opportunity to dock their modules to the ROS.
There is real interest, especially our offer that we are ready not only to train astronauts and carry out space tourism, but we are ready to go as far in cooperation as partners are capable of, up to creating separate modules in their interests, organizing national experiments.
However, Russia is also developing some projects on its own. For example, it is conducting independent lunar solo programs.
For this purpose, work is underway on super-heavy carriers that can deliver the appropriate cargo and, in the future, form a lunar station, as well as move on to the practical use of the Earth's satellite resources.
They are not limited to the Moon: Roscosmos, together with the Academy of Sciences, is already forming research programs for Venus and Mars.
Read materials on the topic:
Russian heavy rocket "Angara-A5" is undergoing control electrical tests
Hydrogen peroxide rocket engine developed in Russia
Docking, survival, training: Russian cosmonauts will have a new training center
Now on home

The 136 hp engine successfully started at -30 ℃

Experts visualized heavy vehicles of the future

The main feature of the exhibit is its ability to move under its own power

Specialists from SUSU and NPO "NTES" took into account logistics needs: the weight of the cargo is displayed in real time

The new method provides a temperature regime for drones in the aircraft's cargo compartment
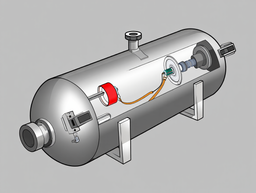
The main purpose of the development is to store and supply working fluids to the pipelines

Combat vehicles transformed into APCs with serious drone protection

"ODK-Klimov" Reduces Financial Claims Against Kazan Helicopter Plant

Russian scientists have recorded a fresh flare zone in the south of the Sun

Army's "Boomerang-10" Implements Target Acquisition Function

The price of the aircraft without engines starts from 233 million rubles

The operation takes only 12 seconds per wheel