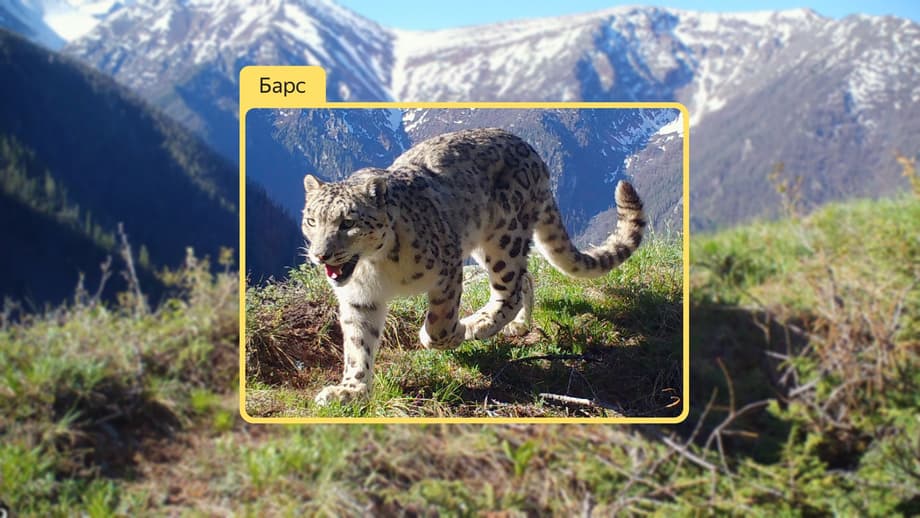
In the Saylyugemsky National Park in the Altai Republic, a neural network helps to recognize red-listed snow leopards, manuls, argali, red deer, ibex, and other local animals on camera traps.

A project capable of helping scientists study animals in their natural, hard-to-reach habitat and protect them was developed by Yandex Cloud with the support of the Yandex School of Data Analysis (SDA).
The neural network, trained to recognize snow leopards and other animals in photos and videos, analyzes data from camera traps throughout the national park, which occupies 118,000 hectares.
Instead of weeks of manual work by a person on data from photo and video traps, it does it in a few seconds. AI sorts images into folders with different types of animals: bears in one folder, manuls in another, hares in a third, and so on.
In some cases, the model indicates several options for what it "sees." In the next stage, the neural network will learn to identify specific individual leopards in the images by their appearance. This way, scientists will be able to save resources, effort, and more effectively study and conserve snow leopards and other animals.
Leopards will be recognized by the unique pattern on their fur. Also, in the future, the company is considering how to add advanced data analysis and visualization to the neural network. They will help collect statistics on snow leopards and other inhabitants of the park, build a map of their favorite places, and study their routes of movement using the neural network.