The journal Magnetochemistry published an article describing the development of scientists from the Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine (ICBFM) SB RAS, carried out jointly with scientists from Guangzhou Medical University. Researchers have created nanocapsules for drug delivery to tumors.
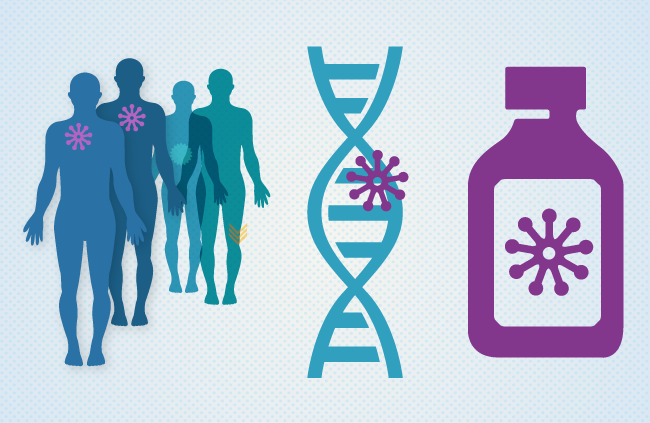
We obtained magnetic nanoparticles, stabilized them with nylon, and then dissolved the magnetic particle inside this composite with acid treatment. As a result, we were left with only a nylon shell with a void inside. In aqueous conditions, this capsule swells, and substances get inside. The article shows that it has a sufficiently large capacity for loading a drug inside.
Biodegradable and non-toxic polymer nylon-6 (capron) was used to work with nanoparticles. The nylon coating not only stabilizes the particles, but also makes it possible to attach additional compounds to them. For example, you can attach a ligand — a molecule that will provide targeted delivery of nanocapsules directly to tumor cells.
We plan to assemble the base, and when it is already shown that both the carrier, the drug, and the targeting component are presented in one set that is stable and non-toxic, it will be possible to start in vivo studies.
Now on home
Previously, drawings resembling Geely Monjaro appeared online, sparking rumors of cooperation

Journalist Alexey Kostylev faces up to 10 years in prison

A corresponding bill has been submitted to the State Duma

The products of the Samara plant are intended, among other things, for shipbuilding and mechanical engineering

Direct laser deposition and selective laser sintering were used in the production

"Buk-M3", S-300, "Tor-2", and "Pantsir" systems are capable of engaging this long-range cruise missile

The devices were manufactured by the Institute of Physical and Technical Problems

The enzyme system in the composition dissolves soft plaque and destroys bacteria

In terms of this indicator, the country is second only to Iraq, Iran and Saudi Arabia

The increase in prices for spare parts is explained by inflation, logistics and the aging of the car fleet

Fake messages were distributed from an unreliable address
