The first artificial satellite in human history was launched into orbit 68 years ago by the R-7 rocket from the Tyuratam test range (now the Baikonur Cosmodrome), marking October 4, 1957, as the starting point of the Space Age.
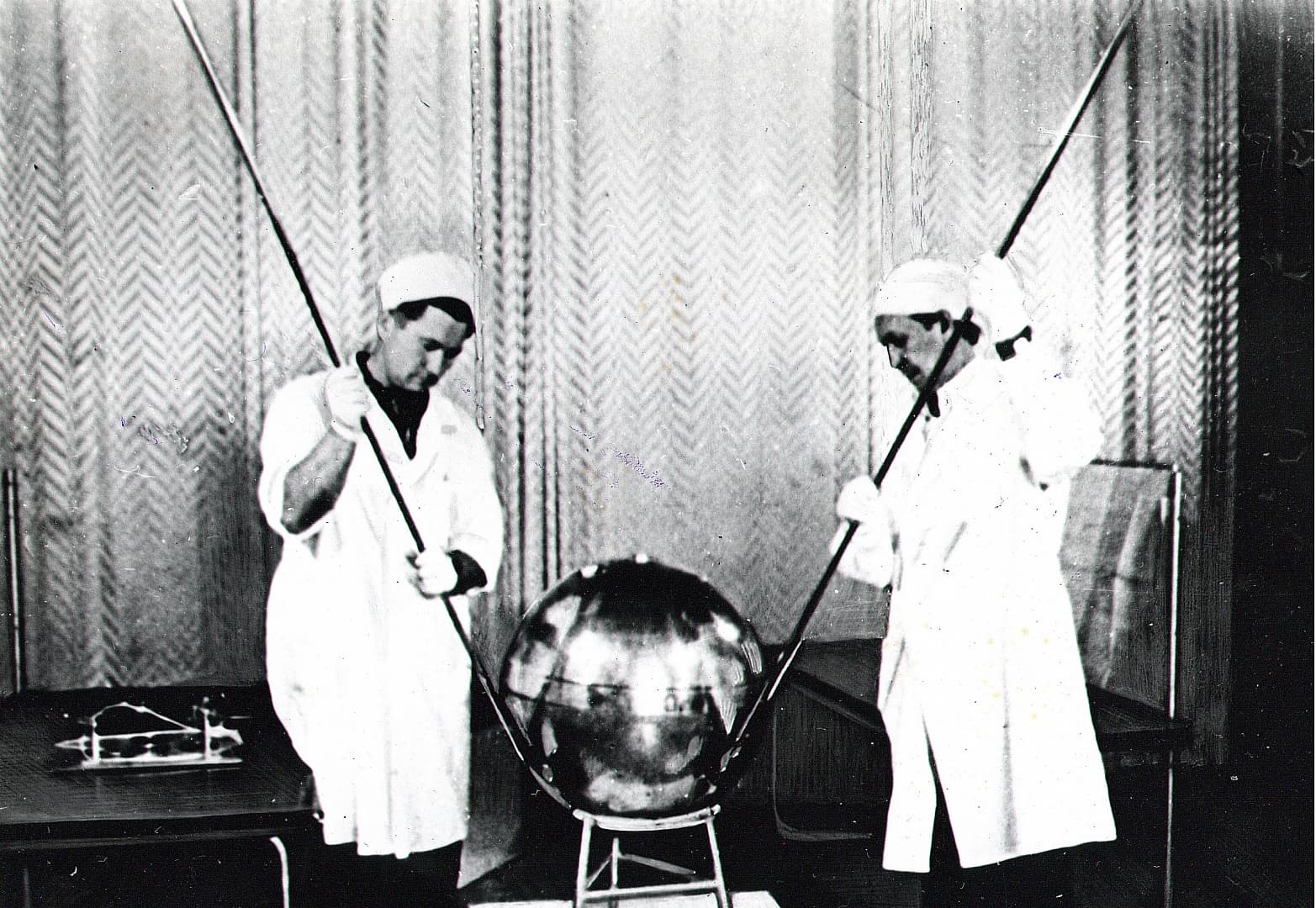

What Did the First AES Look Like?
A sealed aluminum sphere with a diameter of 58 cm, equipped with four antennas, had the most necessary minimal set of equipment inside: a radio station, a block of silver-zinc batteries, a fan for the temperature control system, temperature and pressure sensors, and an on-board cable network. The total weight of the capsule with equipment was 83.6 kg.
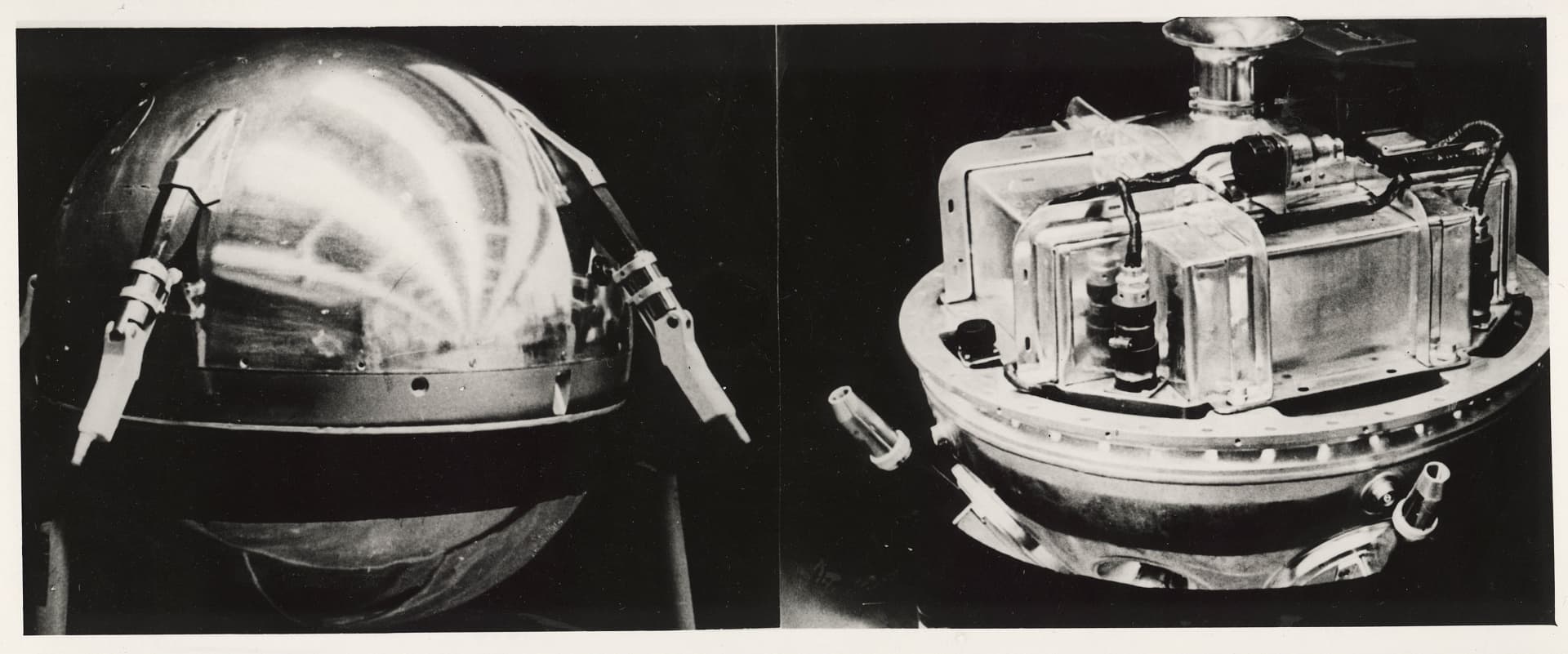
How Did It Happen?
On October 4, 1957, at 22:28 Moscow time, the R-7 rocket was launched, and after 295 seconds, the first AES and the second stage of the rocket were placed into an elliptical orbit, and on the 315th second after the launch, the AES separated from the rocket stage. Transmitters started working, and the whole world heard the famous signals of the first man-made object in human history that flew in near-Earth orbit.
Radio signals from the satellite were received at distances of up to 10-12 thousand km. The first artificial Earth satellite existed for 92 days, completing 1440 orbits around the Earth. On January 4, 1958, as a result of natural braking, it entered the dense layers of the atmosphere and ceased to exist.
Results of the Historical Event
Analysis of the received radio signals from the satellite allowed scientists to study the upper layers of the ionosphere, which was not possible before. Important information was obtained about the operating conditions of the satellite equipment, all calculations were verified, and the density of the upper atmosphere was determined by the satellite's deceleration as it descended from orbit.
The launch of the first Earth satellite and its flight received an overwhelming global response. Thousands of radio amateurs around the world, along with special stations, followed the satellite. Thus began the era of space achievements and the race for world leadership in space.
Read more materials on the topic:
Now on home

Start of deliveries scheduled for 2027

Over 51,000 new motorcycles were sold in Russia in 2025

The car will take at least a year to assemble

The application's audience has reached 20 million users

The model will be included in the list of cars for taxis, price - from 2.25 million rubles

All parking lots of the "Administrator of the Moscow Parking Space" are connected to the service

The cars will be supplied to the Moscow Transport Service Directorate

Deliveries to India may begin in 2028

The technology provides automated search for all types of defects in power units

The plane flew 500 km, accelerating to 425 km/h

The plant stated that the information about the termination of purchases for models 6 and 8 is not true

Scientists are using the "Ekran-M" installation
Articles
-
Russian An-124 "Ruslan" Stuck in Canada for 4 Years and Accrues Millions in Fines
26 Jan 2026
-
Coaxial Propellers: How Counter-Rotation Increases Turboprop Engine Efficiency
25 Jan 2026
-
Kazan Aviation Plant Breaks Old System: Tu-214 to be Assembled Like Cars
25 Jan 2026
-
How Engineers and Technicians Are Paid Today in the Russian Aviation Industry: An Overview with Figures
24 Jan 2026