One of the most powerful flares in recent times occurred in the northeastern part of the Sun on July 15, 2025. As a result of a colossal ejection of solar plasma (coronal mass ejection), a giant crack formed on the surface of the star - the so-called "fiery canyon," about 400,000 km long. This is about the same distance as from Earth to the Moon.
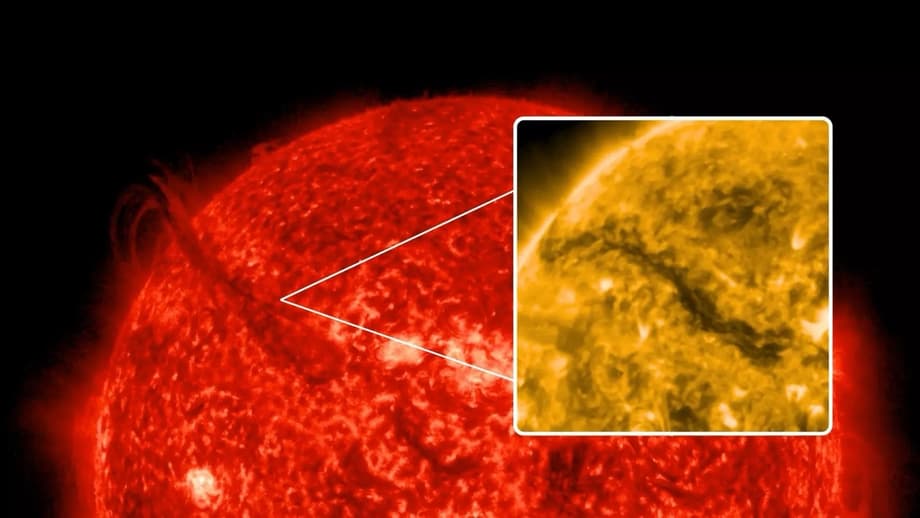
The phenomenon was recorded by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. The height of the walls of this plasma canyon reached 20,000 km. Such phenomena occur when the magnetic fields of the Sun abruptly rearrange after a flare - and leave behind a luminous "scar" of incandescent matter.
Such flares can trigger geomagnetic storms that can affect satellite communications, power systems, and navigation. Although this particular flare does not threaten Earth, the Sun's activity itself is increasing - and scientists are closely monitoring its consequences.
Read more on the topic:
"Kitten" Appeared on the Sun: Earth Continues to Fall into a Coronal Hole, Solar Wind Intensified











