Climate models compiled in the West since 2022 without taking into account data from Russia are a waste of time, as they are unreliable. This was stated by climatologists from Denmark, Finland, Great Britain and the USA, participants in the INTERACT research project.

How climate models work
A climate model, which helps to judge climate change, is compiled on the basis of data from all over the globe. They are included in a digital model for forecasting. Indicators of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, land, soil cover, and glaciers are taken into account. With the help of complex mathematical calculations, changes are calculated in certain time intervals.
Arctic Monitoring
The Arctic is called the "weather kitchen" of the Earth. Cyclones are formed here, melted ice feeds the Atlantic, and ice cover cools the entire planet. The accuracy of data for climate models depends on understanding the processes that occur in the Arctic region. These issues are also dealt with by the Arctic Council, an international forum promoting cooperation in the Arctic. Since 2023, Russia has not been invited to council events.
Today, there is not a single joint international project in the Arctic with the participation of universities or scientific organizations from Russia
She explained that 21 of the 95 ground stations of the INTERACT project are located in Russia. Against the background of sanctions, Western scientists do not receive data from the Russian side.
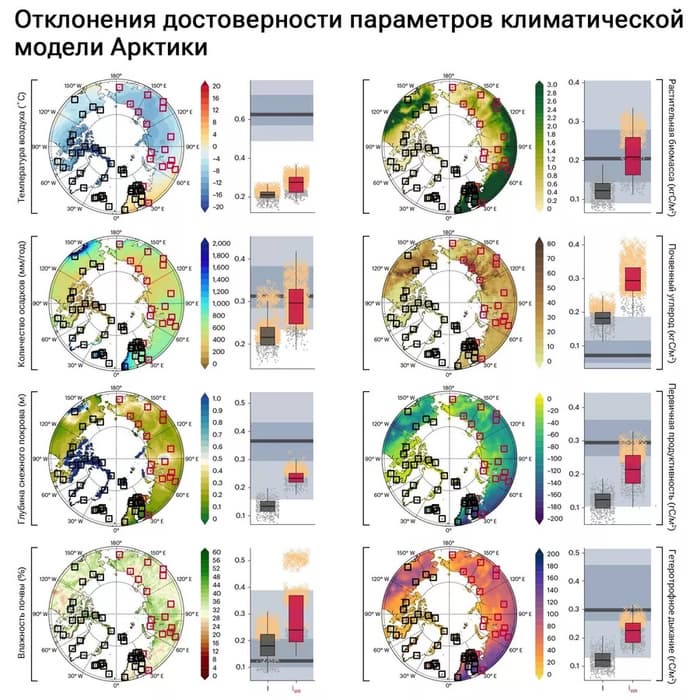
In fact, INTERACT is doing useless work. Their unreliable conclusions are used by specialists from the World Meteorological Organization, the International Council for Science and other departments. Climatologists from Denmark, Finland, Great Britain and the USA, involved in INTERACT, emphasized that the international scientific community should create monitoring programs that are representative of the entire Arctic, and this cannot be done without data exchange with all countries, including Russia.
Roscosmos receives information about the situation in the Arctic from the new hydrometeorological satellite "Arktika-M" No. 2, launched into space in mid-December 2023.
Now on home

Foreign delegation visited the "Parus electro" electrical equipment manufacturing plant

"The new system is more powerful than the existing version"

Sergey Marzhetsky stated that placing orders in the DPRK could become a realistic solution under sanctions

NDTV: India Aims to Acquire 40 Combat Aircraft

The autonomous platform can travel up to 60 km

Casting technology allows creating elements with geometry that cannot be obtained by other methods

The manufacturer promises compliance with global safety and quality standards

Remterminal to establish rolling stock production by 2032

Inside - Sleeping Places for Four, Shower, Toilet, and Hot Water

The device is equipped with BAM-OS 18×55 gas cylinders with red hot pepper

Almost 70% of cars in the country have exceeded the 10-year mark

The complex will start operating as early as 2026