At Tomsk Polytechnic University, scientists from the School of Non-Destructive Testing and Security Engineering are working on domestic software to accelerate the development of ultra-sensitive sensors — microelectromechanical inertial sensors (MEMS). Representatives of the Element Group of Companies ordered and help to carry out the work, they are most interested in modernizing the development of gyroscopes and accelerometers.
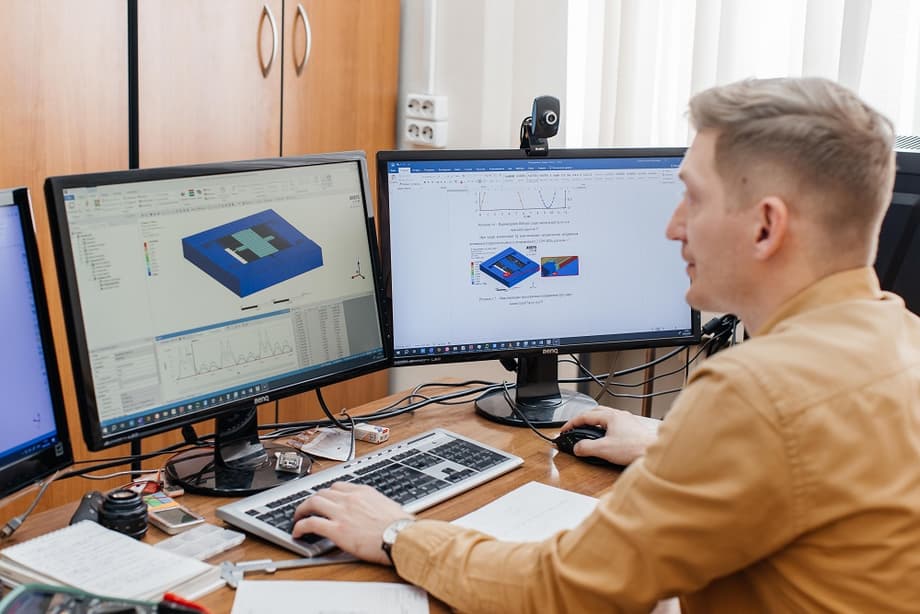

MEMS themselves are devices with interconnected mechanical and electrical components of micron size. They can analyze humidity, speed, magnetic field and other parameters. For example, a gyroscope measures the angular velocity of an object, and an accelerometer measures its acceleration. MEMS allow you to control moving objects, without them the development of automotive, aviation, shipbuilding, and rocket engineering is impossible. Also, MEMS are an integral part of unmanned vehicles, robotics, the creation of drill bits for oil production, stabilization of optical systems and communication control systems, and are used in other industries.
The development, testing and manufacturing of MEMS is a lengthy and time-consuming process. The software from Tomsk residents will help automate the development of MEMS designs and designs. In particular, it will make it possible to preliminarily create computer 3D models of future sensors and adjust them according to the required characteristics and parameters.
Using the software, MEMS developers will be able to create models of both the entire device and its individual elements. Based on mathematical models, the program will generate a ready-made design of the sensor being developed. Thus, the software will allow modeling the mechanical and electrical phenomena that occur during the operation of these devices, and determine how technological and temperature disturbances affect the characteristics of the devices being developed. All this will reduce the economic and time costs of producing navigation, positioning and stabilization systems for moving objects.
It is assumed that the software will be universal and suitable not only for designing gyroscopes and accelerometers, but also for designing other sensors. It can be integrated into Russian micromechanics production lines, and thus localize part of high-precision instruments in Russia for the development of technological sovereignty.
Read materials on the topic:
Russia is testing a new diamond gyroscope for drones – it will be able to work even in space
Russian lasers will become even better and more accurate – a way has been found to modernize them
Russian scientists have created an engine for small satellites that runs on vodka
Ural "Multiklet" asks the Russian government for 20 billion rubles for a factory
Now on home

Герой России Гарнаев: никто из профессионалов о возобновлении производства на КАЗ всерьёз не говорит

Система отслеживает спутники на высотах до 50 000 км и ведёт за ними наблюдение

The armored vehicle is equipped with a KamAZ-740.35-400 diesel engine with a power of 400 hp.

Constant improvements in avionics, weapons and tactical capabilities will make the aircraft a flexible response to future challenges

The exterior of the KamAZ-54901 features fairings on the cab and chassis for fuel economy

Fighters are in demand both domestically and abroad

Tyazhpromexport and Venezuela Agree on Plant Revival

The company not only completed the state order, but also quickly mastered the production of AK-12K for special forces
Experts have developed a photogrammetric complex with a resolution of less than 1 cm


