The new "Arktika-M" spacecraft has been delivered to Baikonur. This is a series of the world's first meteorological satellites exploring the Arctic region from a highly elliptical orbit. The first "Arktika-M" was launched into its target orbit in February 2021.
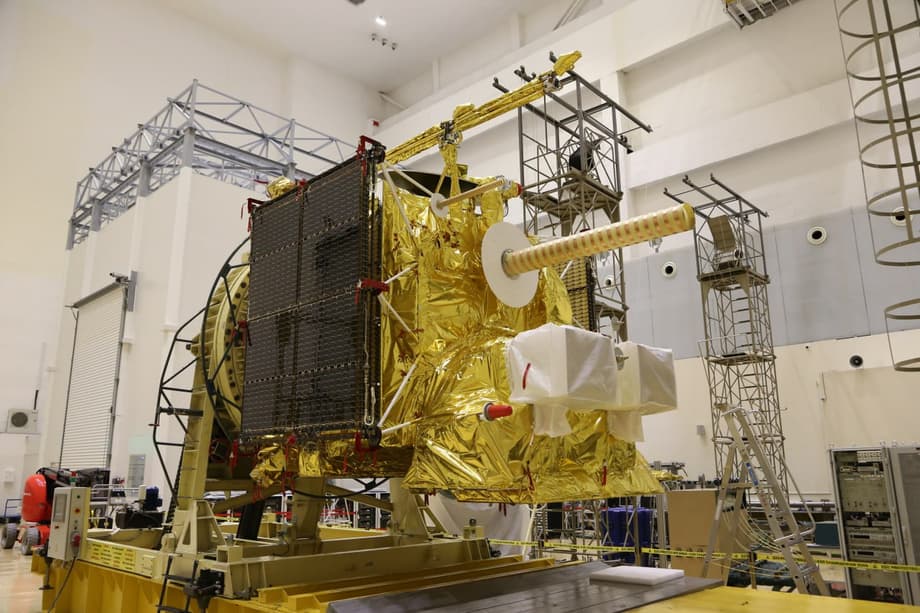

Prior to this, the "Arktika-M" No. 2 spacecraft had already passed a series of tests. In particular, comprehensive electrical tests of the disassembled and assembled product, its thermoelectric tests in a vacuum chamber, and technological vibration tests were conducted. Now it is ready for launch in December.
Two "Arktika-M" spacecraft as part of the system will provide round-the-clock monitoring of the surface and cloud cover of the Earth and seas in the Arctic region and adjacent territories, as well as constant and reliable exchange of meteorological information and transmission of signals to rescue services about the location of distressed ships and aircraft within the framework of the international search and rescue system "COSPAS-SARSAT".
Initially, the system was supposed to have two spacecraft, but in May 2023, a state contract was concluded to modernize the "Arktika-M" system to four units in orbit.
The modernized "Arktika-M" with four satellites will provide observation of the polar region from different angles.
This will help to detail ultra-short-term weather forecasts, promptly monitor dangerous natural phenomena and emergencies, and also increase the accuracy of identifying clouds over snow and ice cover and determining their characteristics.
Such data contribute to the development of meteorology, hydrology, agrometeorology, climate and environmental monitoring in the Arctic region. For Russia, this means a more dynamic development of the Northern regions.